1.Collecting Accurate, Refined, Relevant Data from Variety of Sources
Data that is specific and relevant to eCommerce falls under several categories:
-
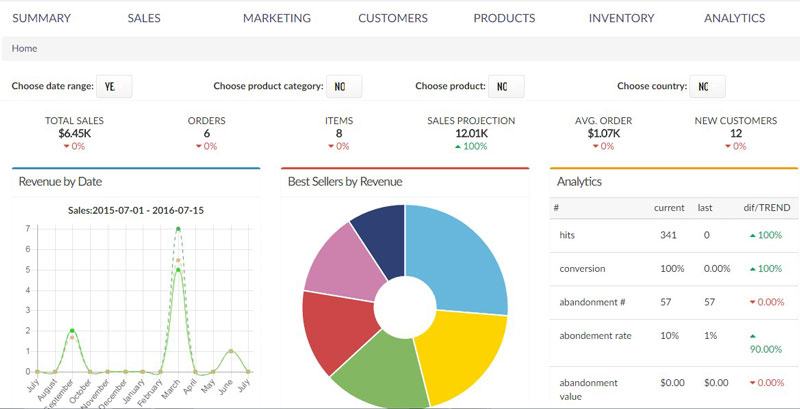
Inventory. Detailed information about stock levels of a product in real time, are essential. What is the stock in different locations, at different periods of the year? Were there any shortages, or overstocks? Identifying best selling products, as well as periods of the year when customers are more likely to buy them.
-
Staff. We need to know in real time, how many employees we have, how they are allocated, how they perform in the means of sales volume and profitability. At what periods of the year, month, day we have shortages of workforce, in which locations, on which positions?
-
Customers. Predictive analytics in eCommerce collects information about customer interests. These information give the answers to questions like: what customer likes, what are his interests, how he shops and when, what moves him and makes him decide to purchase - quality, price, special offers, availability of products, fast shipping, what kind of goods he likes and purchases often, at what periods of the year, month, day he submits his purchases and much more. Customers sometimes cut back on their purchases, and we need to know how often that happens and why.
Product ratings and reviews are also a great way to learn about customer's feelings about products and services. They give us customer opinions and sentiment as psichological drivers of their shopping behavior. For active marketing campaigns, we want to know which advertising messages drive more customers decide to buy our products.
For better understanding of customer behavior, the focus should rather be put on Big Data, than on customers. We want to measure actual behavior of customers instead of their behavioral intent. It is simple to explain: it is much more relevant for supporting our decisions in sales business to know what customers actually did, than what the wnated or planned to do. Because, the frist had already happened, and the second might never happen. Great eCommerce site is capable of recording every move consumers make - during their buying process, and even when they don't purchase goods, giving us relevant data to work with.
This allows sales businesses to theoretically create a profile for each customer based on their behavior and buying history, among other things.
-
Sales history and projections. As we said, our eCommerce site records a wide variety of data, including the sales history from the first day of its existance. In every moment we know the details about sales from the last year, month, week, day, hour. We have valuable data from the past for comparison with current performance of our Online Store. We know the sales volume nd profits, depending on the product, period, customer, location, price, special offers. We are then able to implement advanced dashboards and define KPI's (Key Performance Indicators), performance metrics and the belonging monitoring system.
-
Demographics. Where do our customers come from? What's their gender, age, level of education, occupation? How does our sales depend on this?
- Competition. Our competition is active, just as we are. Most of the companies in sales business have already implemented eCommerce. We are aware of the ongoing trend of making Online Stores mobile friendly, and optimized to perform in the best possible way on all devices, from desktops, over laptops, to tablets and smart phones. Are our competitors optimized? Are we? Do they have advanced eCommerce features, and which of them are better than ours? What are their prices? Do they provide special offers, discounts, promotions, personalized selling, how, and when? Which products are their top sellers?
All mentioned information helps us integrate operational, spreadsheet, and historic data, that is visually appealing, easy to use and grasp, and prepared (by relevance) to be put under strong muscles of Predictive Analytics and its advanced algorithms.
2. Creating, refining, evaluating, deploying and monitoring models for Predictive Analysis
-
Set clear business goals (big or small): a) to increase revenue, b) to increase profit, c) to reduce shipping or warehouse expenses, d) to recommend items to upsell or crossell. Knowing the goals will set the foundation for aligning daily operations of the Online Store Management with predefined strategic objectives.
-
Prepare the data for predictive analysis. This includes determination of inputs (variables) from raw data, for use in the Predictive Analytics algorithm. According to Predictive Analytics Times, this process consists of two key components. First is creation and derivation of fields/variables from raw data. And second is filtering-out process that identifies the set of variables to be considered within a Predictive Analytics solution.
-
Create the predictive model, refine and evaluate it
-
Deploy the model
- Monitor the effectiveness of the model
Comments
Very informative arricle.
Very informative arricle. Thank you!